Elasticsearch客户端Kibana安装使用
Kibana是一个开源的分析与可视化平台,设计出来用于和Elasticsearch一起使用的。你可以用kibana搜索、查看存放在Elasticsearch中的数据。Kibana与Elasticsearch的交互方式是各种不同的图表、表格、地图等,直观的展示数据,从而达到高级的数据分析与可视化的目的。
Elasticsearch、Logstash和Kibana这三个技术就是我们常说的ELK技术栈,可以说这三个技术的组合是大数据领域中一个很巧妙的设计。一种很典型的MVC思想,模型持久层,视图层和控制层。Logstash担任控制层的角色,负责搜集和过滤数据。Elasticsearch担任数据持久层的角色,负责储存数据。而我们这章的主题Kibana担任视图层角色,拥有各种维度的查询和分析,并使用图形化的界面展示存放在Elasticsearch中的数据。
Kibana 用户手册: https://www.elastic.co/guide/cn/kibana/current/introduction.html
Kibana登录: http://192.168.241.142:5601/app/dev_tools#/console
1、安裝
注意:Elasticsearch和Kibana的版本需要对应。
下载地址 :https://www.elastic.co/cn/downloads/past-releases#kibana

2.安装
因再es安装目录 所以用es用户
下载Kibana放在 elasticsearch 同级目录中
[root@bogon src]# wget [root@bogon src]# tar -zxvf kibana-8.12.2-linux-x86_64.tar.gz [root@bogon src]# mv kibana-8.12.2 /usr/localkibana812/
进入/usr/localkibana812/config目录,
[root@bogon kibana812]# cd config/ [root@bogon kibana812]# vim kibana.yml server.port: 5601 server.host: "0.0.0.0" # 此处不能写“localhost”,否则访问不了kibana elasticsearch.hosts: ["http://192.168.241.142:9200"] #这里是elasticsearch的访问地址
登录 Kibana不能使用root用户
[root@bogon kibana812]# chown -R cc:cc /usr/local/kibana812/ [root@bogon bin]# su cc
3.启动Kibana
1、进入bin目录,
[cc@bogon kibana812]# cd bin/
2、前台启动 (关闭服务 关闭窗口 或者ctrl+c)
[cc@bogon bin]$ ./kibana
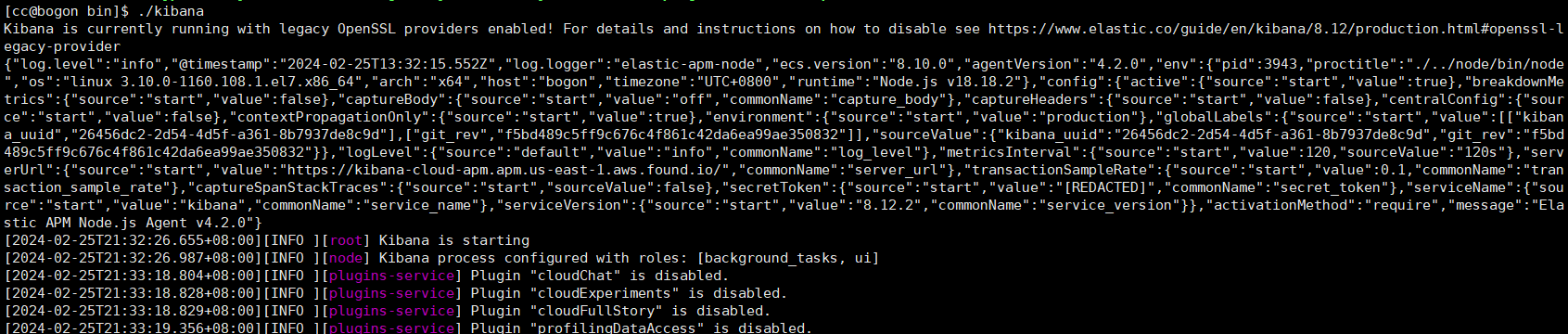
后台启动
nohup ./bin/kibana & 关闭服务 根据端口查进行 然后 kill掉 lsof -i:5601 会出多个 kill 第一 [object Object]
4、页面访问
ip:5601
访问 : http://192.168.241.142:5601/
5. 关于索引的基本操作
当然不是只有 kibana可以测试,使用其他软件如 Postman或者T alend APTTester都可以。
我这里使用的 kibana.
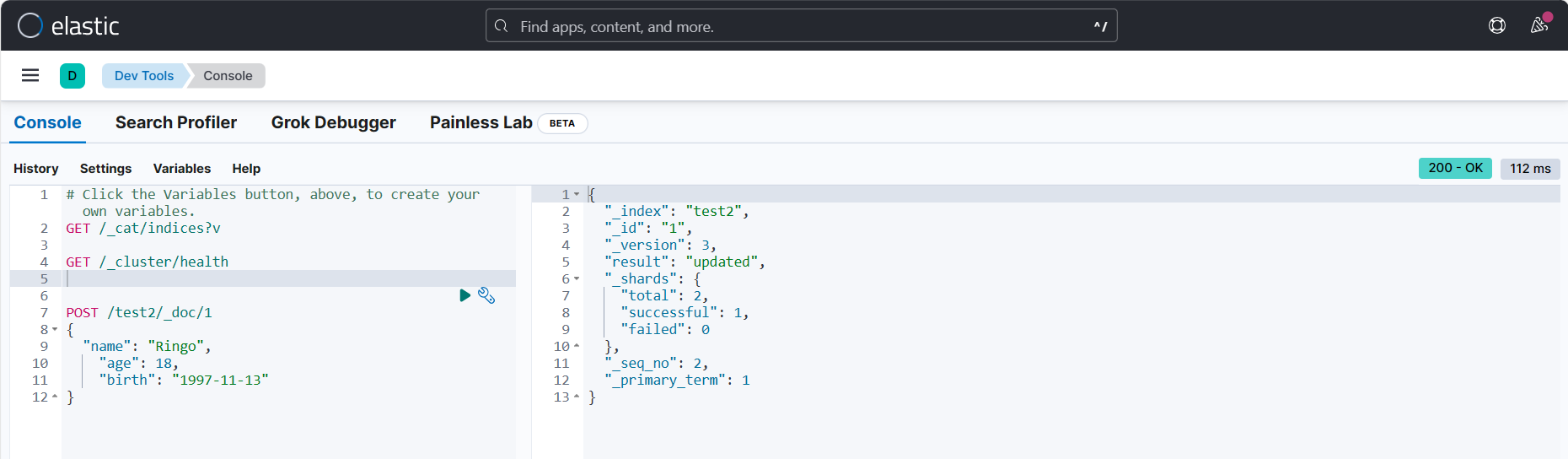
1、创建索引并添加数据
# 在kibana输入
POST /test2/_doc/1
{
"name": "Ringo",
"age": 18,
"birth": "1997-11-13"
}
2、我们自己没有为索引写mapping映射查看索引默认的信息
GET /test1
或
GET请求 192.168.241.142:9200/test2
# 返回的结果,ES给我们的字段自动加上了类型
{
"test2": {
"aliases": {},
"mappings": {
"properties": {
"age": {
"type": "long"
},
"birth": {
"type": "date"
},
"name": {
"type": "text",
"fields": {
"keyword": {
"type": "keyword",
"ignore_above": 256
}
}
}
}
},
"settings": {
"index": {
"routing": {
"allocation": {
"include": {
"_tier_preference": "data_content"
}
}
},
"number_of_shards": "1",
"provided_name": "test2",
"creation_date": "1708997613196",
"number_of_replicas": "1",
"uuid": "TUsCx7TnRgq5Z6XK3Ltg_w",
"version": {
"created": "8500010"
}
}
}
}
} 如果自己的文档字段没有指定类型,那么 elasticsearch就会给我们默认配置字段类型!
2.关于文档的基本操作
# 1、创建文档
POST请求 http://39.97.3.60:9200/ringo/_doc/1
{
"name": "RingoTangs",
"age": 18,
"describe": "铃铃铃",
"tags": ["阳光","喜欢篮球","喜欢学习"]
}
# 2、获取数据
GET请求
# 3、更新数据,PUT如果不写全字段就会被覆盖
PUT请求 http://39.97.3.60:9200/ringo/_doc/3
{
"name": "李四233",
"age": 30,
"describe": "法外狂徒,李四",
"tags": ["靓仔","喜欢唱歌","喜欢学习"]
}
# 4、推荐使用POST来更新,自由度很高,携带的JSON可以只写修改字段
POST请求 http://39.97.3.60:9200/ringo/_doc/3/_update
{
"doc": {
"name": "李四999"
}
}3、简单查询
GET请求 或 GET /ringo/_search?q=name:李四 GET请求 http://39.97.3.60:9200/ringo/_search?q=tags:篮球
4、复杂查询
# 1、带上查询条件,match只要名字中有"张三"的都会被检索出来
POST请求 http://39.97.3.60:9200/ringo/_search
{
"query": {
"match": {
"name": "张三"
}
}
}
# 2、查询结果返回具体的字段,使用"_source"
POST请求 http://39.97.3.60:9200/ringo/_search
{
"query": {
"match": {
"name": "张三"
}
},
"_source": ["name", "age"]
}
# 3、查询结果排序,使用"sort",通过某个字段进行排序
POST请求 http://39.97.3.60:9200/ringo/_search
{
"query": {
"match": {
"name": "张三"
}
},
"_source": ["name", "age"],
"sort": [{
"age": {
"order": "asc"
}
}]
}
# 4、分页查询 "from"从哪里开始,“size"每页显示几条数据
POST请求 http://39.97.3.60:9200/ringo/_search
{
"query": {
"match": {
"name": "张三"
}
},
"_source": ["name", "age"],
"from": 0,
"size": 1
}
# 5、通过"bool"和"must"组合使用,可以多条件组合查询,等价于and
# 会把name="张三"和age=30的文档查出来
POST请求 http://39.97.3.60:9200/ringo/_search
{
"query": {
"bool": {
"must": [{
"match": {
"name": "张三"
}
}, {
"match": {
"age": 30
}
}]
}
}
}
# 4、"should"有一个条件符合即可,等价于or
# 会把name="张三"或者age=18的文档查出来
POST请求 http://39.97.3.60:9200/ringo/_search
{
"query": {
"bool": {
"should": [{
"match": {
"name": "张三"
}
}, {
"match": {
"age": 18
}
}]
}
}
}
# 5、"must_not"查询年龄不是18岁的人
POST请求 http://39.97.3.60:9200/ringo/_search
{
"query": {
"bool": {
"must_not": [{
"match": {
"age": 18
}
}]
}
}
}
# 6、查询结果过滤,范围查询
# gt:大于
# gte:大于等于
# lt:小于
# lte:小于等于
POST请求 http://39.97.3.60:9200/ringo/_search
{
"query": {
"bool": {
"must":[{
"match": {
"name": "张三"
}
}],
"filter": {
"range": {
"age": {
"gt": 19
}
}
}
}
}
}
# 7、多条件使用空格隔开,只要满足其中一个结果就可以被查出
POST请求 http://39.97.3.60:9200/ringo/_search
{
"query": {
"match": {
"tags": "喜欢 阳光"
}
}
}
# 8、精确查询term "term"输入的词不会被分词,"match"会使用分词器解析
# term查询是直接通过倒排索引指定的词条进行精确查找的!
# 注意:keyword类型的字段不会被分词器解析!!!
PUT /testdb
{
"mappings": {
"properties": {
"name": {
"type": "text" # text类型会走分词器
},
"describe": {
"type": "keyword" # keyword不会走分词器,当成一个整体
}
}
}
}
GET /testdb/_search
{
"query": {
"term": {
"describe": "Ringo 每天都要好好学习"
}
}
}
# 9、高亮查询
# 测试样例
GET /testdb/_search
{
"query": {
"match": {
"name": "棠时"
}
},
"highlight": {
"pre_tags": "<p class='key' style='color:red'>",
"post_tags": "</p>",
"fields": {
"name": {}
}
}
}
# 结果
"highlight" : {
"name" : [
"<p class='key' style='color:red'>棠</p><p class='key' style='color:red'>时</p>每天都要开心"
]
} other
#查询所有索引
GET /_cat/indices?v
#查询健康
GET /_cluster/health
#单机情况下是不需要设置副本分区数。调整副本分区数为0
PUT _settings
{
"index" : {
"number_of_replicas" : 0
}
}
#创建索引
PUT user
{
"mappings" : {
"properties" : {
"age" : {
"type" : "integer"
},
"name" : {
"type" : "text"
},
"name2" : {
"type" : "keyword"
},
"name3" : {
"type" : "text",
"fields" : {
"keyword" : {
"type" : "keyword",
"ignore_above" : 256
}
}
},
"hobby" : {
"type" : "text"
}
}
}
}
#查询索引 类型
GET user/_mapping
#查询索引下所有文档
GET user/_search
#添加文档
PUT user/_doc/1
{
"age": 18,
"name": "张三风",
"name2": "张三风",
"name3": "张三风",
"hobby": "爱吃饭,爱钓鱼"
}
PUT user/_doc/2
{
"age": 18,
"name": "张三",
"name2": "张三",
"name3": "张三",
"hobby": "爱吃饭,爱钓鱼,爱祖国"
}
#按条件查询 类型 keyword查询时条件只能全匹配 text全文索引查询,查询时会先分词,然后用分词去匹配查询
#keyword+text类型,一个字段两种类型,可以全匹配,也可以全文索引查询
# keyword
GET user/_search
{
"query": {
"term": {
"name2": {
"value": "张三"
}
}
}
}
# text 使用match
GET user/_search
{
"query": {
"match": {
"name": "张三"
}
}
}
#keyword+text查询例子,name3(text+keyword)的查询。
GET user/_search
{
"query": {
"term": {
"name3.keyword": {
"value":"张三"
}
}
}
}
#keyword+text查询例子 当想用全文索引查询时,用match
GET user/_search
{
"query": {
"match": {
"name3": "张三"
}
}
}
#创建索引的时候,text类型如果没指定使用分词器,就会默认内置的分词器,所以使用ik分词器时,创建索引时需要指定。
PUT user2
{
"mappings" : {
"properties" : {
"age" : {
"type" : "integer"
},
"name" : {
"type" : "text",
"analyzer": "ik_max_word",
"search_analyzer" : "ik_max_word"
},
"name2" : {
"type" : "keyword"
},
"name3" : {
"type" : "text",
"fields" : {
"keyword" : {
"type" : "keyword",
"ignore_above" : 256
}
},
"analyzer": "ik_max_word",
"search_analyzer": "ik_max_word"
},
"hobby" : {
"type" : "text",
"analyzer": "ik_max_word",
"search_analyzer" : "ik_max_word"
}
}
}
}
#把user的数据复制到user2。
POST _reindex
{
"source":{
"index":"user"
},
"dest":{
"index":"user2"
}
}
#次查询user “爱祖国”,得到2数据 因采用默认分词器。
GET user/_search
{
"query": {
"match": {
"hobby": "爱祖国"
}
}
}
#再次查询user2 “爱祖国”,得到一条想要的数据,没有多余数据。证明ik分词在索引中生效了。
GET user2/_search
{
"query": {
"match": {
"hobby": "爱祖国"
}
}
}
#查询原因
GET /_cat/shards?h=index,shard,prirep,state,unassigned.reason
#返回未分配索引每个分片的详情和未分配的原因,
GET /_cluster/allocation/explain?pretty
#查看设置
GET /newsinfo/_settings
#重置分片
PUT /newsinfo/_settings
{
"number_of_replicas": 0
}
#重新分配
PUT /newsinfo/_settings
{
"number_of_replicas": 2
}
#查看分词器 默认
POST _analyze
{
"analyzer": "standard",
"text": "我是中国人"
}
#ik ik_smart 最少切分算法
POST _analyze
{
"analyzer":"ik_smart",
"text":"我是中国人"
}
#ik ik_max_word 最细粒度切分算法
POST _analyze
{
"analyzer":"ik_max_word",
"text":"我是中国人"
}
#设置ik分词器
PUT school_index
{
"settings" : {
"index" : {
"analysis.analyzer.default.type": "ik_max_word"
}
}
} 附:
https://blog.csdn.net/pyfysf/article/details/131448092
本文为崔凯原创文章,转载无需和我联系,但请注明来自冷暖自知一抹茶ckhttp://www.cksite.cn

- 最新评论
- 总共0条评论

